Applications of Memory Alloy Stents in Vertebral Fractures
Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) are prevalent injuries that can lead to significant pain, reduced mobility, and diminished quality of life. Traditional treatments, such as percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, have been effective but come with limitations, including the risk of cement leakage and insufficient restoration of vertebral height. In response to these challenges, our study explores the use of nitinol memory alloy stents as a novel approach to treating VCFs.
Study Overview
This research aimed to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of using nitinol memory alloy stents in the management of VCFs. Nitinol, known for its superelasticity and shape memory properties, offers the potential to provide dynamic support to fractured vertebrae, promoting better stabilization and alignment.
Methodology
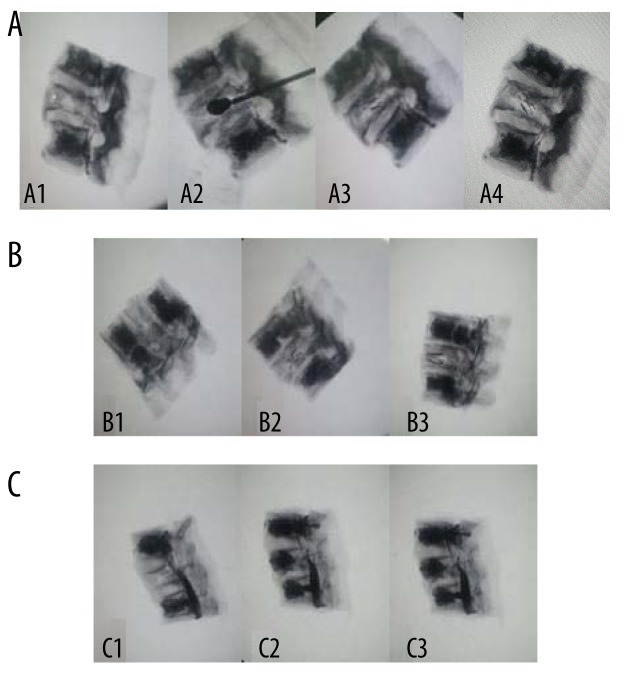
In our study, patients with diagnosed VCFs underwent a minimally invasive procedure where nitinol memory alloy stents were implanted into the affected vertebral bodies. The stents were designed to expand within the vertebral body, providing internal support and aiding in the restoration of vertebral height. Postoperative evaluations included imaging studies to assess vertebral alignment and patient-reported outcomes to gauge pain relief and functional improvement.
Findings
The implantation of nitinol memory alloy stents resulted in significant restoration of vertebral height and alignment. Patients reported substantial pain relief and improved mobility in the postoperative period. Importantly, the procedure demonstrated a low incidence of complications, with no significant cases of cement leakage or adjacent vertebral fractures observed during the follow-up period.
Conclusion
The use of nitinol memory alloy stents presents a promising advancement in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. By providing internal support and promoting vertebral height restoration, these stents can enhance patient outcomes and reduce the risks associated with traditional treatments. Further studies with larger patient populations and longer follow-up periods are warranted to fully establish the efficacy and safety profile of this innovative approach.